The graphics card is the most important component of a gaming PC, largely determining the level of gaming performance your PC can deliver. Your CPU, memory, and storage play a part, sure, but they’re much less critical as far as gaming is concerned. While you can very well decide between the best gaming GPUs without knowing anything about their specifications, it always helps to be more informed.
The most important GPU specifications will enable you to better grasp the ongoing conversations around new graphics card releases and how to separate marketing from fact.
How to check which GPU you have in 6 simple ways
Windows has more than enough built-in tools to help you identify your GPU
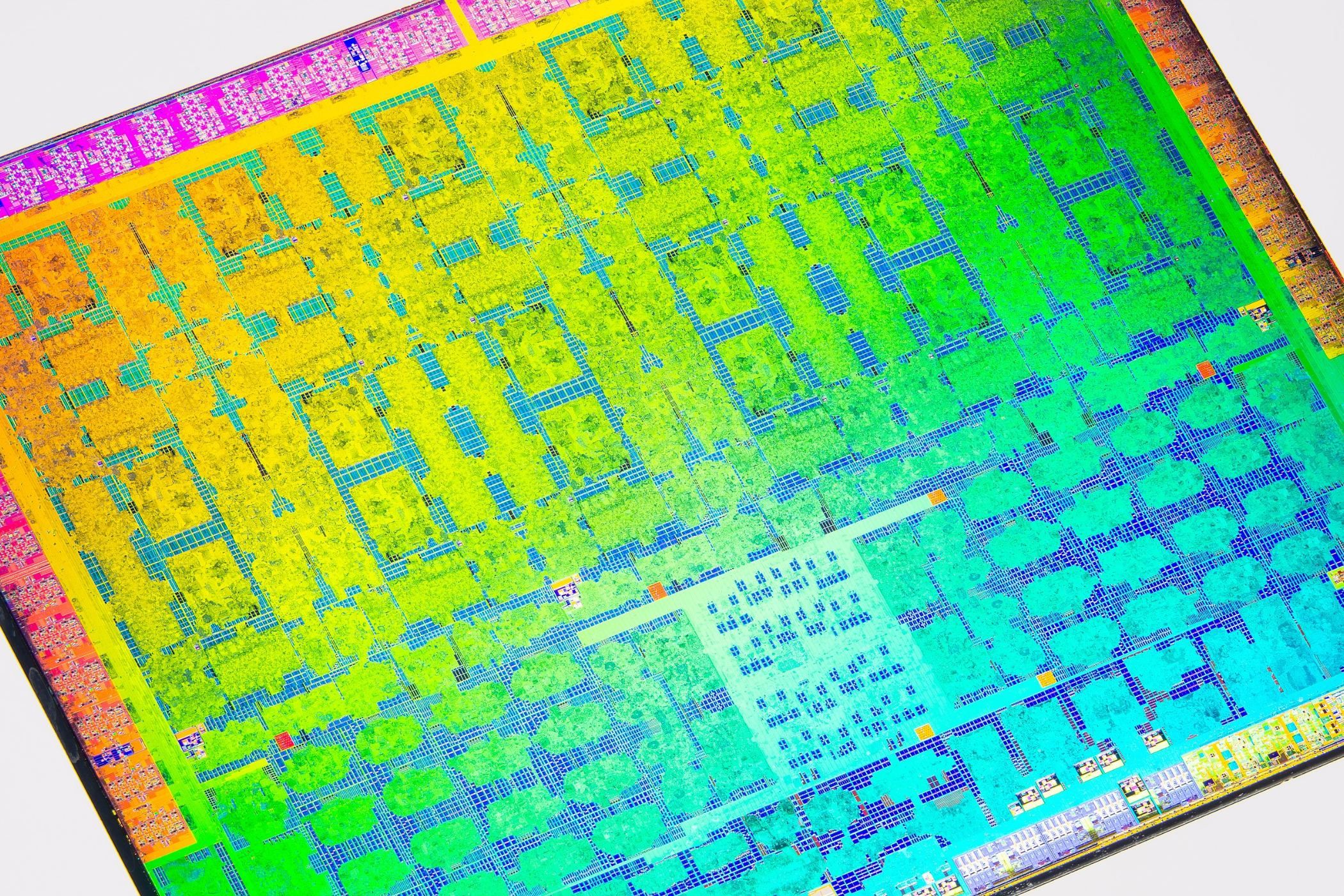
GPU die
GPU or graphics card — what’s in a name?
Your graphics card is technically not the same as the GPU. Every graphics card has a GPU die soldered on the PCB inside it, around which the heatsink, shroud, and fans are assembled. This GPU die is the actual graphics processor responsible for the performance of your gaming PC. GPU manufacturers produce 4 to 5 GPU dies per generation, which are then tweaked and cut down depending on the specific SKU in the lineup.
For instance, the RTX 4070 and RTX 4070 Super have the same AD104 GPU inside them but the Super variant has more CUDA cores unlocked. Newer generations of GPUs use more advanced fabrication nodes to fit more and more transistors within the same die area. There’s a lot more to it, but the smaller process node (in nanometer) your GPU is manufactured on, the better it’s likely to be.
7 worst GPUs of all time
There are bad GPUs, and then there are GPUs that we’ll never forget because of how disastrous they were.
GPU “cores”
10,000 cores? Not exactly
Just like your CPU, your GPU also has multiple cores within it, but they’re not comparable to CPU cores. GPUs are composed of thousands of processing elements or “cores” arranged in clusters. These clusters are then grouped into what are known as compute units, and are capable of executing millions of instructions simultaneously, unlike CPU cores and threads that handle one complex instruction per thread at a time.
CUDA cores shouldn’t be mistaken for physical cores like on a CPU.
Now, every company terms their compute units differently — AMD calls them Compute Units (thankfully), Nvidia calls them Stream Multiprocessors, and Intel calls them Xe-cores. You can’t compare the compute units of different manufacturers directly due to underlying differences in the architecture and how each company classifies various specifications. These metrics only work when comparing different models within the same GPU generation of the same manufacturer.
The “CUDA cores” that are prominent in Nvidia’s marketing are the general-purpose processing elements within the compute units, and shouldn’t be mistaken for physical cores like on a CPU. Similarly, Tensor cores and Ray Tracing cores are specialized processing units featured on newer Nvidia GPUs. The best GPUs for deep learning owe their performance to such specialized AI-focused cores.

How do graphics cards work under the hood
Learn how most modern GPUs work to deliver those buttery-smooth frames while gaming
Memory size, type, and bus width
VRAM isn’t the only factor
You might be familiar with GPU memory or VRAM. It’s one of the most recognizable GPU specs, with many consumers mistaking it for the most important specification in their buying decision. The VRAM size (in GB) is the amount of visual memory on a graphics card that’s responsible for retaining the framebuffer, texture information, and other graphical data. If your GPU runs out of available VRAM, you’ll encounter performance slowdowns or visual artifacts.
The memory size, type, and bus width together determine the GPU’s total bandwidth.
The memory type also matters for GPU performance. Modern graphics cards feature faster and more power efficient GDDR6 or GDDR6X memory, while older models will have GDDR5 memory. Lastly, memory bus facilitates the data transfer between the GPU and VRAM. A greater bus width will allow faster data transfer which is especially important at higher resolutions and during complex GPU-intensive tasks.
The memory size, type, and bus width together determine the GPU’s total bandwidth, measured in GB/s.

How much VRAM do gamers need in 2023?
Unfortunately, having enough VRAM on your GPU is a luxury today.
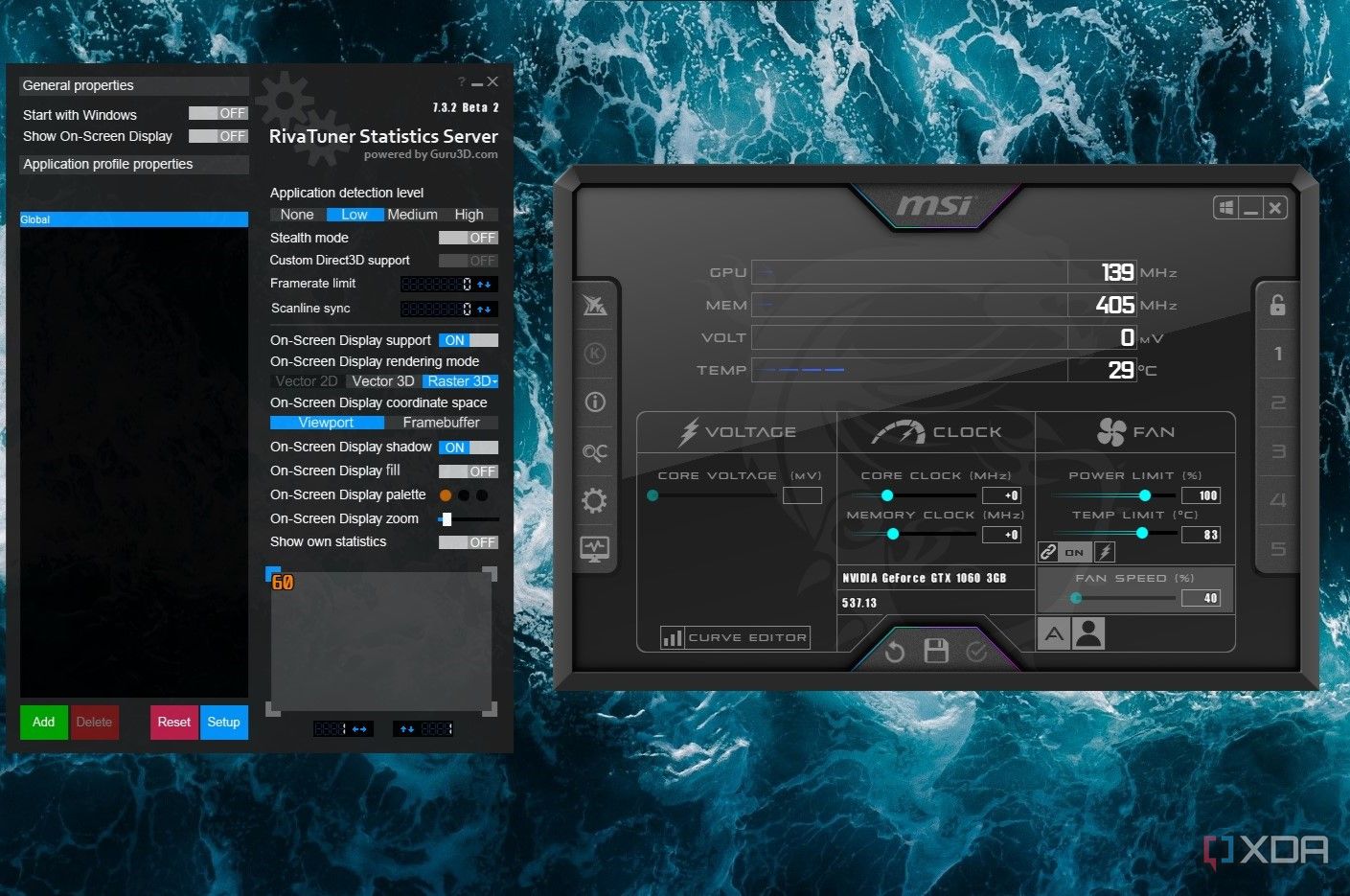
Clock speeds
How fast does your GPU think?
Similar to CPUs, GPUs also have clock speeds — more than one, in fact. There’s the core clock and memory clock. The core clock is the speed at which the GPU processes instructions and processes graphically-intensive tasks. The memory clock, on the other hand, is the speed at which the GPU memory (VRAM) can send or receive data to or from the GPU.
Faster clock speeds will generally result in faster operations and a smoother experience, whether during gaming or other workloads. Both the core clock and memory clock can be tweaked, also known as overclocking your GPU.
TDP or TGP
How hot is too hot?
The TDP or TGP of your graphics card is the total amount of power it can consume under regular working conditions. For instance, an RTX 4070 Super will generally not draw more than 220W of power from the power supply. Momentary spikes might push the power draw beyond the TGP, but that only lasts for micro-seconds.
The TGP also indicated how hot your GPU will run. The more demanding the load, the more the power draw, and the more the heat produced. As long as you’re not seeing anything beyond 90°C when checking your graphics card temperature, there’s no cause for concern.

How to connect a GPU to the PSU
Get your connections right to get the best performance out of your GPU
FP32 performance
Get a theoretical idea about GPU performance
FP32 or floating-point single precision is one of the standard ways for measuring compute performance for GPUs. It gives us a theoretical way to compare performance among GPUs from various manufacturers and generations. Measured in teraflops (TFLOPS), FP32 indicates how many floating-point operations a GPU can perform in a second. 1 TFLOP equals one trillion floating-point operations per second.
For instance, an RTX 3080 has an FP32 performance of 29.77 TFLOPS, whereas the number for the RTX 4080 Super is 52.22 TFLOPS. You can compare this to an even older card, such as the RTX 2080 Ti which has 13.45 TFLOPS of FP32 performance. TFLOPS might represent mathematical performance of a GPU, but it doesn’t tell the whole picture. Other factors affect GPU performance as well, but FP32 performance is still a helpful metric to get a general idea about how powerful a GPU is.
Other specs
Not critical but good to know
Besides the specs discussed above, there are other aspects of a GPU that won’t make or break your purchase decision but might impact what applications you use it for. First, PCIe support of your GPU is something that won’t affect your day-to-day usage by any significant margin. But you should know that GPUs supporting PCIe 4.0 vs those supporting PCIe 3.0 will have access to greater bandwidth, which will likely become an advantage in the future.
You might want to check which version of upscaling tech your GPU supports.
Second, your GPU’s API support i.e. DirectX, Vulkan, and OpenGL support can influence your gaming performance. But this only matters if you’re comparing a really old GPU to a modern one, as most newer GPUs will come with support for all popular 3D graphics and compute APIs.
Third, you might want to check which version of upscaling tech your GPU supports. The DLSS or FSR or XeSS support of your GPU will greatly impact the FPS you can experience in games. For instance, RTX 30 series cards don’t enjoy official support for Nvidia’s Frame Generation technology due to lacking dedicated hardware that’s present on the newer RTX 40 series cards. Lastly, the display connectors on your graphics card will determine whether you can use HDMI, DP, or both to connect it your display.

3 reasons to pick Nvidia over AMD
There are still some convincing reasons to pick an Nvidia GPU over AMD
GPU specs, numbers, and beyond
While GPU specs and theoretical metrics help you differentiate between various GPU models, real-world testing is still the best way to decide which GPU you should buy for your system. Check reviews for the graphics card you’re planning to buy, compare performance numbers between multiple models in the games you want to play, and narrow down your options based on your budget. And don’t forget to match your CPU and GPU to avoid leaving performance on the table.

7 top GPUs of all time
Of all the great GPUs ever made, there are seven that really stand out.